The after-tax salvage value is calculated as: sv t*sv-bv Accounting homework help

To estimate salvage value, a company can use the percentage of the original cost method or get an independent appraisal. The percentage of cost method multiplies the original cost by the salvage value percentage. Suppose a company spent $1 million purchasing machinery and tools, which are expected to be useful for five years and then be sold for $200k. Each year, the depreciation expense is $10,000 and four years have passed, so the accumulated depreciation to date is $40,000. Starting from the original cost of purchase, we must deduct the product of the annual depreciation expense and the number of years. The useful life assumption estimates the number of years an asset is expected to remain productive and generate revenue.
Product Review: NeuroByte DataMind AI-Powered Backup and Recovery Platform
It is calculated by simply dividing the cost of an asset, less its salvage value, by the useful life of the asset. Terminal Cash Flow is the final cash flow (i.e., Net of cash inflow & cash outflow) at the end of the project. It includes after-tax cash flow from disposing of all the equipment related to the project and recoupment of working capital. The terminal cash flow equation is the final cash flow at the end of the project. Upon sale, the distinction between the sale value and the guide worth determines the acquire or loss, influencing the tax legal responsibility and, consequently, the after-tax salvage worth.
Asset Type
After that, this machine should become obsolete and be replaced by a newer technology machine. In 2022, the depreciation expense recognized on the income statement (and added back on the cash flow statement) was $3 million. Brokerage charges, public sale bills, and different promoting prices immediately cut back web proceeds. Factoring these prices into calculations gives a practical evaluation of the ultimate worth.
Strengths and weaknesses of NPV
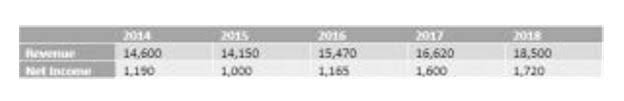
- Thus far, we’ve discussed net capital spending in terms of tracking the trend in capital expenditures and depreciation in analyzing a company’s current (and future) growth profile.
- This distinction between the gross promoting value and web proceeds is essential as a result of solely the online quantity contributes to the ultimate calculation.
- To begin with this manufacturing process, Redtech has to install a new machine, which is expected to have 5 years of economic life.
- Consequently, the after-tax salvage worth might be decrease than if all the acquire have been handled as a capital acquire.
- Depreciation schedules provide a detailed record of how assets depreciate over time, ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards.
If the company estimates that the entire fleet would be worthless at the end of its useful life, the salvage value after tax salvage value formula would be $0, and the company would depreciate the full $250,000. Companies can also use comparable data with existing assets they owned, especially if these assets are normally used during the course of business. For example, consider a delivery company that frequently turns over its delivery trucks.
What is Net Capital Spending?
- Companies estimate salvage value to determine the amount to which an asset’s value is depreciated over its useful life.
- The salvage calculator reduces the loss and assists in making a decision before all the useful life of the assist has been passed.
- It’s also handy for guessing how much money they might make when they get rid of it.
- Under straight-line depreciation, the asset’s value is reduced in equal increments per year until reaching a residual value of zero by the end of its useful life.
- Calculating after-tax salvage value ensures that all tax liabilities are accounted for, providing a true reflection of the asset’s worth.
If a company believes an item will be useful for a long time and make money for them, they might say it has a long useful life. Next, the annual depreciation can be calculated by subtracting the residual value from the PP&E purchase price and dividing that amount by the useful life assumption. There are six years remaining in https://www.bookstime.com/articles/legal-e-billing the car’s total useful life, thus the estimated price of the car should be around $60,000.
- The straight-line method is a commonly used approach for calculating depreciation by evenly spreading the decrease in an asset’s value over its useful life until it reaches its salvage value.
- The straight-line method allocates an equal depreciation expense across each period of an asset’s useful life.
- In this way, it influences capital budgeting decisions by helping determine the total cost of ownership and whether to buy versus lease.
- For example, if a construction company can sell an inoperable crane for parts at a price of $5,000, that is the crane’s salvage value.
- Depreciation is the decrease in value of an asset over time, which is calculated using various methods such as straight-line or accelerated depreciation.
- The chosen depreciation method influences the book value of the asset, impacting the gain or loss on disposal.
Factors Affecting Salvage Value Calculation
Whether leasing a car, buying manufacturing equipment, or managing a fleet of vehicles, understanding residual value puts you in a better position to make sound financial decisions. Terminal cash flow is a critical concept in financial modeling, representing the net cash flow that a project generates at the conclusion of its forecast period. It is essentially the net cash inflow or outflow resulting from the final phase of a project or investment. This phase often marks the end of explicit cash flow projections and is particularly relevant in discounted cash flow (DCF) analyses.

This ensures a precise calculation of depreciation expenses, which ultimately impacts the estimated salvage value. It means that the asset will be depreciated faster than with the straight line method. The double-declining balance method results in higher depreciation expenses in the beginning of an asset’s life and lower depreciation expenses later. This method is used with assets that quickly lose value early in their useful life. A company may also choose to go with this method if it offers them tax or cash flow advantages. Failing to account for depreciation recapture can result in an overestimation of the online proceeds from asset disposal and, consequently, inaccurate monetary projections.
No, after-tax salvage value is the amount of money received from selling an asset after accounting for taxes, unearned revenue while book value is the original cost of the asset minus accumulated depreciation. Calculating the after-tax salvage value is crucial for businesses to accurately assess the financial impact of selling their assets. The after-tax salvage value is more than an accounting footnote—it shapes investment decisions and tax strategies. By mastering its calculation, financial managers ensure accurate project valuations and compliance with tax laws. Whether using straight-line or MACRS depreciation, the key is consistency and precision.

The after-tax Salvage Value is calculated as: SV – t*(SV-BV)
Understanding the definition and significance of salvage value helps business owners and managers make informed choices and plan for the future. In the following sections, we will explore the exact meaning of salvage value and delve into its relevance in business operations. Companies estimate salvage value to determine the amount to which an asset’s value is depreciated over its useful life. By subtracting the salvage value from the original cost, companies can calculate the carrying value of the asset after depreciation.